(Credit: eoline.com)
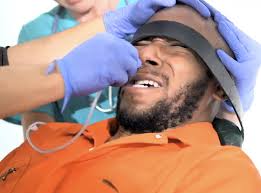
In April, when a hunger strike by detainees at the prison in Guantánamo Bay, Cuba, was in its third month, Pentagon officials agreed with defense lawyers that the underlying cause was a growing despair among prisoners who have been in detention for a decade with no hope of getting out. The protest, which at its height involved 106 of the 166 prisoners there this summer, served to put the Guantánamo issue back on the radar in Washington.
The National Defense Authorization Act for 2014, signed on Thursday by President Obama, includes a long-sought provision easing the Pentagon’s ability to transfer to countries other than the United States detainees rated as low threats. Mr. Obama, who has wavered on his early vows to shut down the prison, praised Congress for this change, though he stressed that the prison remained a blight on the nation’s reputation.
The improved transfer policy helps, but a petty policy change at the prison this month shows how perverse the situation has become. The military says it will no longer report the number of prisoners on hunger strike, according to a report in the Miami Herald. A spokesman for the facility said the military “will not further their protests by reporting the numbers to the public.” The numbers of detainees being force-fed by prison authorities, which dropped into the teens in recent months, offered the world a window into the prison, which has been shrouded in secrecy even though its motto is “safe, humane, legal, transparent detention.”
Eighty-six of the remaining prisoners — more than half — were designated three years ago for transfer to another country, provided that security concerns could be satisfied. Yet the transfer plan was left adrift in the face of political combat. Even if the new defense bill spurs progress in reducing the detainee population, the delivery of credible justice for those at the Guantánamo prison camp is far from complete.

